
If this is not possible, then an anteroposterior view will be taken. Required projections can vary by country and hospital, although an erect posteroanterior (PA) projection is typically the first preference. Lateral views of the chest are obtained in a similar fashion as the posteroanterior views, except in the lateral view, the patient stands with both arms raised and the left side of the chest pressed against a flat surface. As a result, most supine films are also AP. In this situation, mobile X-ray equipment is used to obtain a lying down chest x-ray (known as a "supine film"). AP chest x-rays are harder to read than PA x-rays and are therefore generally reserved for situations where it is difficult for the patient to get an ordinary chest x-ray, such as when the patient is bedridden. In anteroposterior (AP) views, the positions of the x-ray source and detector are reversed: the x-ray beam enters through the anterior aspect and exits through the posterior aspect of the chest. A radiation source is positioned behind the patient at a standard distance (most often 6 feet, 1,8m), and the x-ray beam is fired toward the patient. To obtain this view, the patient stands facing a flat surface behind which is an x-ray detector. In a posteroanterior (PA) view, the x-ray source is positioned so that the x-ray beam enters through the posterior (back) aspect of the chest and exits out of the anterior (front) aspect, where the beam is detected.

The most common views are posteroanterior, anteroposterior, and lateral. alveolar air space disease with prominent vascularity with or without pleural effusionsĭifferent views (also known as projections) of the chest can be obtained by changing the relative orientation of the body and the direction of the x-ray beam. Fields ( lung parenchyma), being evidence of alveolar flooding.apices for fibrosis, pneumothorax, pleural thickening or plaques
#Normal lung xray free#
evidence of free air, indicative of perforation of an abdominal viscus

The main regions where a chest X-ray may identify problems may be summarized as ABCDEF by their first letters: Unless a fractured rib is suspected of being displaced, and therefore likely to cause damage to the lungs and other tissue structures, x-ray of the chest is not necessary as it will not alter patient management. When a condition is suspected based on chest radiography, additional imaging of the chest can be obtained to definitively diagnose the condition or to provide evidence in favor of the diagnosis suggested by initial chest radiography. įor some conditions of the chest, radiography is good for screening but poor for diagnosis. Chest radiographs are also used to screen for job-related lung disease in industries such as mining where workers are exposed to dust. Pneumonia and congestive heart failure are very commonly diagnosed by chest radiograph.
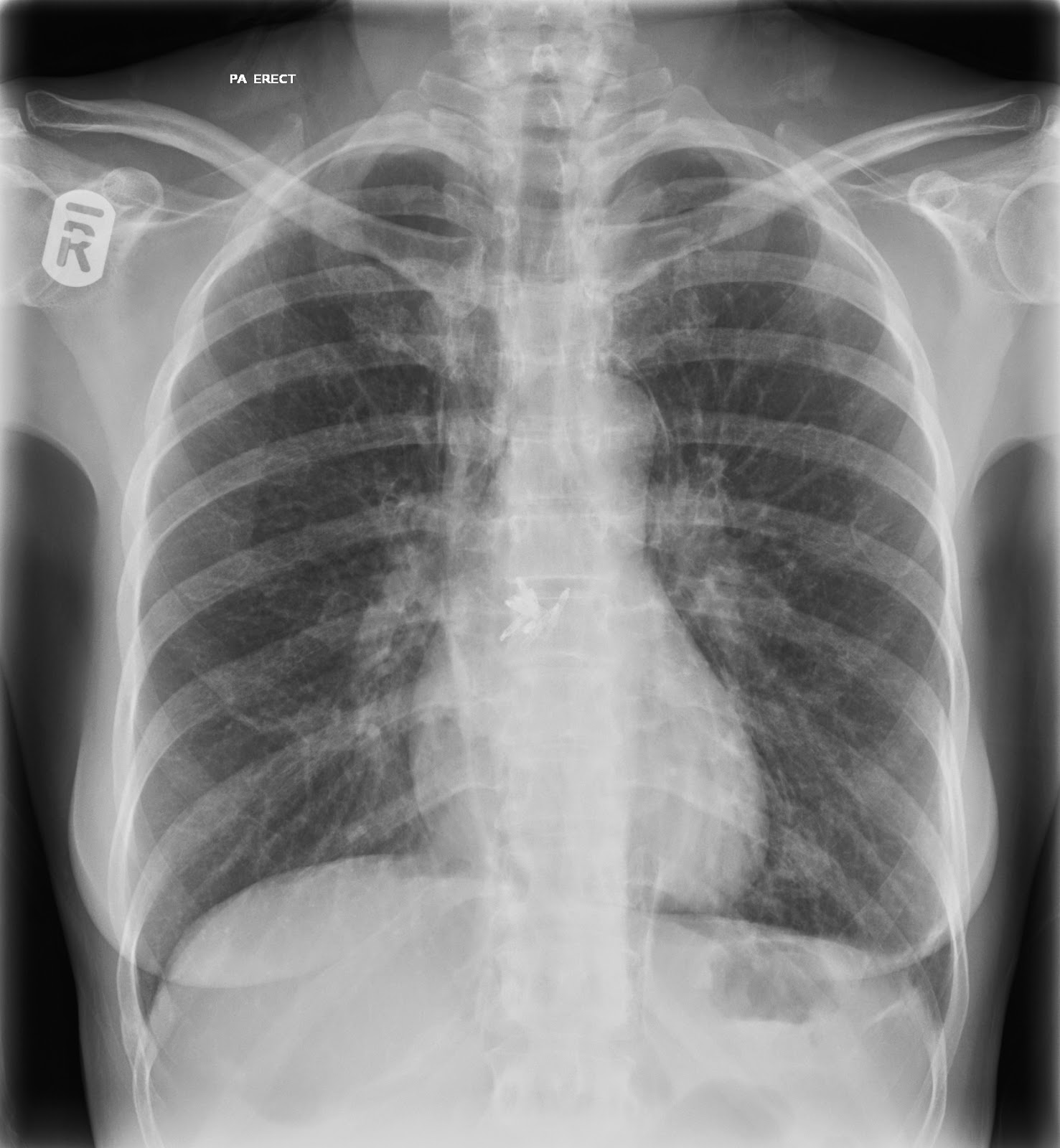
Conditions commonly identified by chest radiographyĬhest radiographs are used to diagnose many conditions involving the chest wall, including its bones, and also structures contained within the thoracic cavity including the lungs, heart, and great vessels.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
